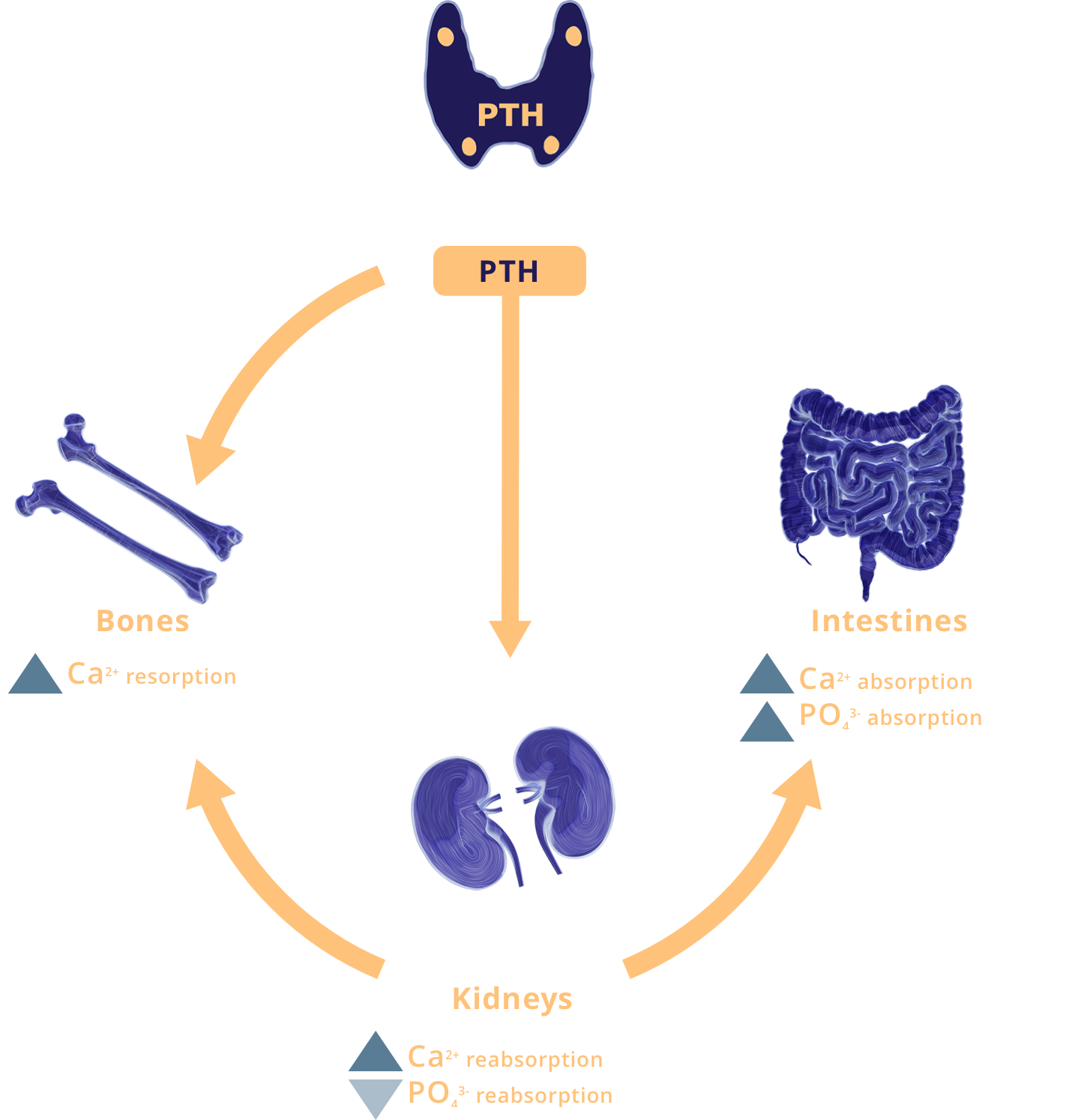
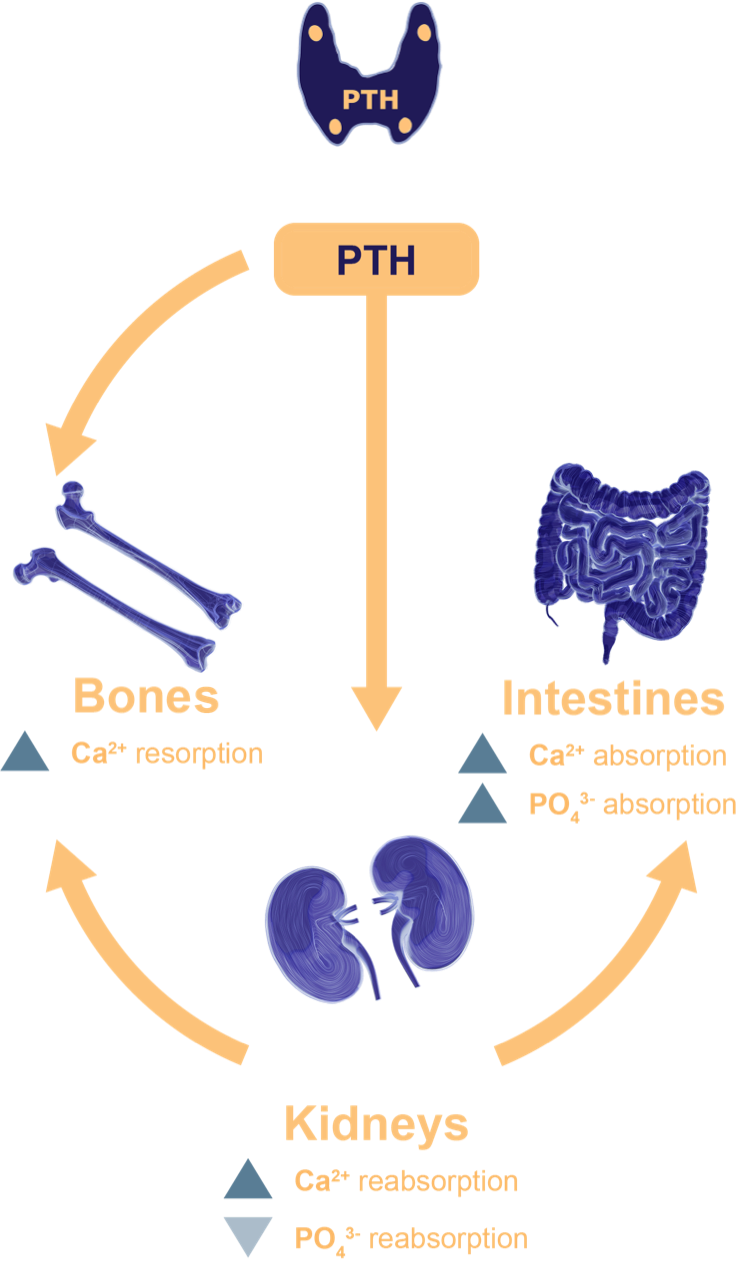
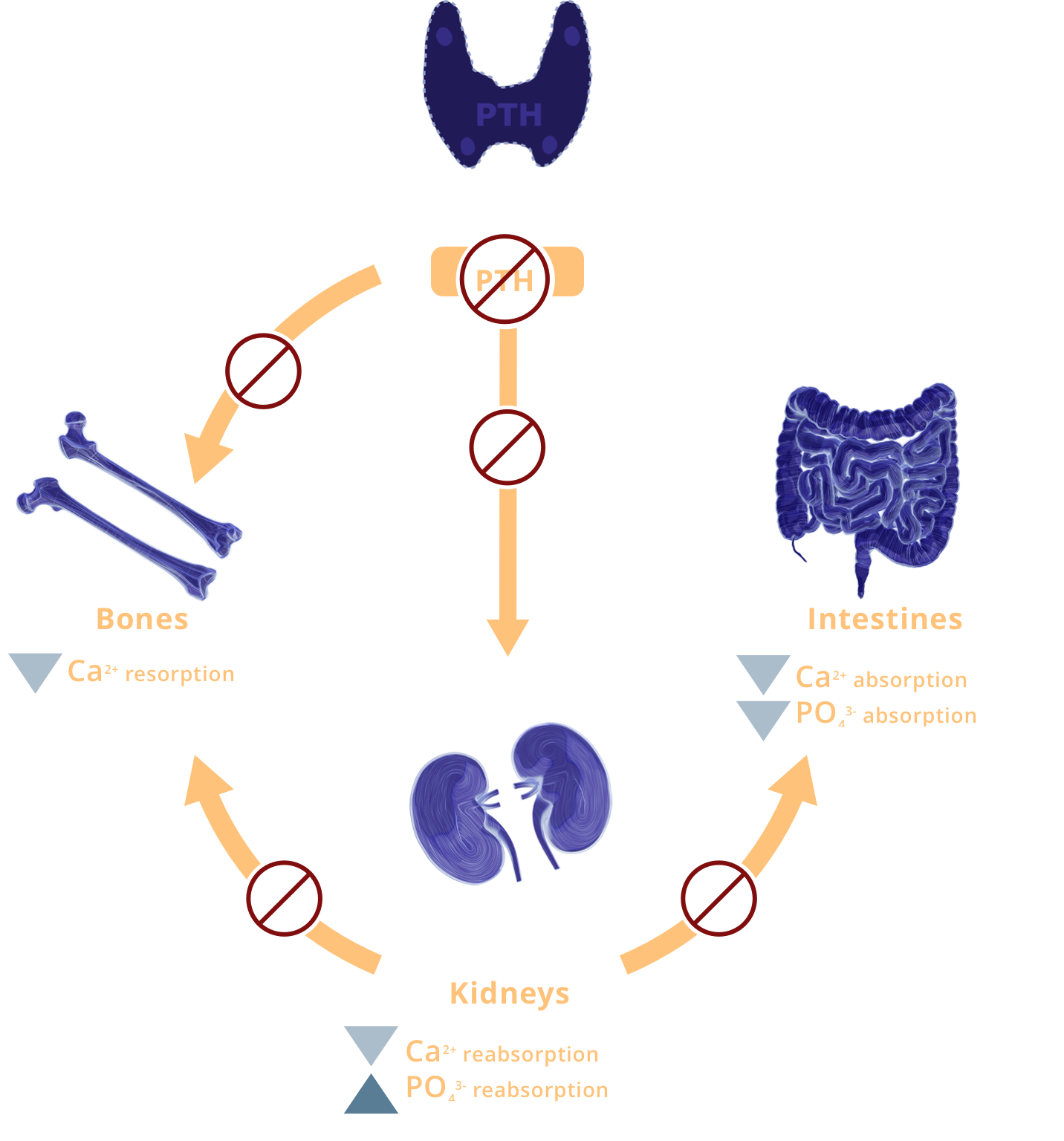
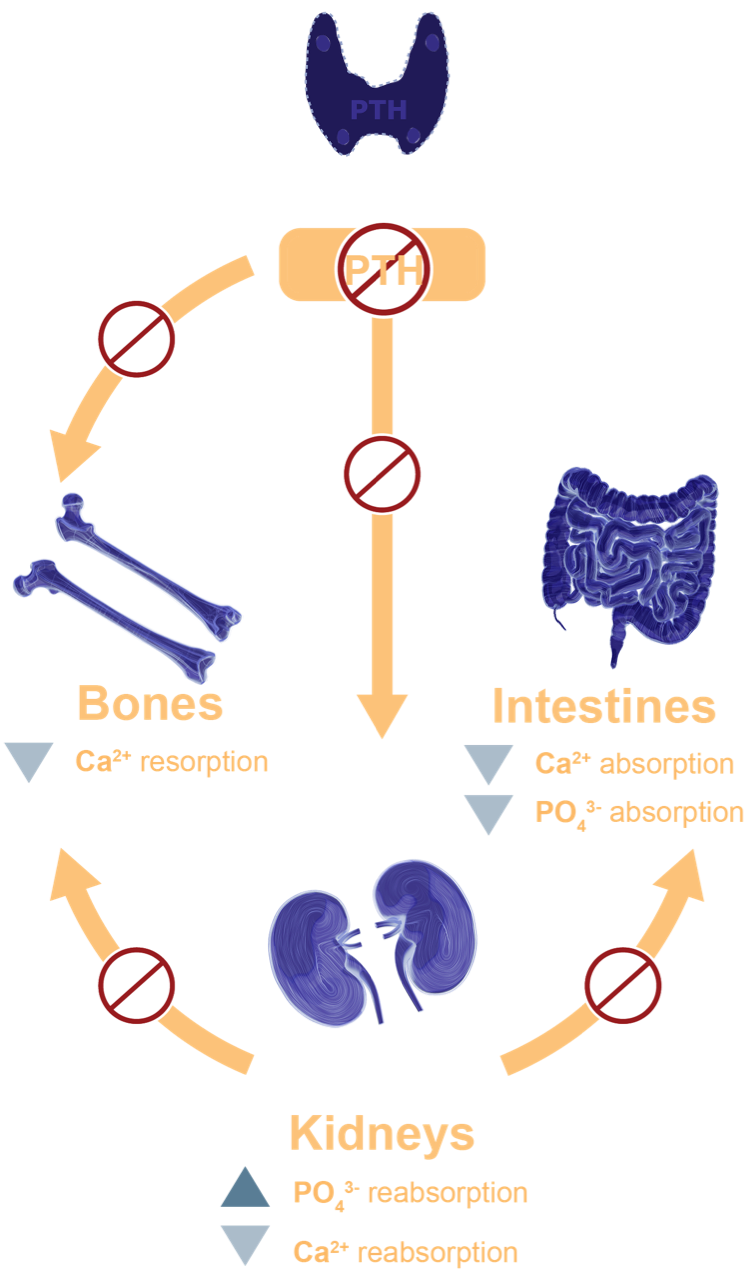
Pathophysiology
Hypoparathyroidism Is Characterized by the Absence or Deficiency of Parathyroid Hormone1,2
Effects of Hypoparathyroidism on Renal Function6-8

- The renal dysfunction associated with hypoparathyroidism results in downstream complications, including hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, and hypercalciuria1,6,7
PTH Deficiency Leads to Reduced Bone Turnover2
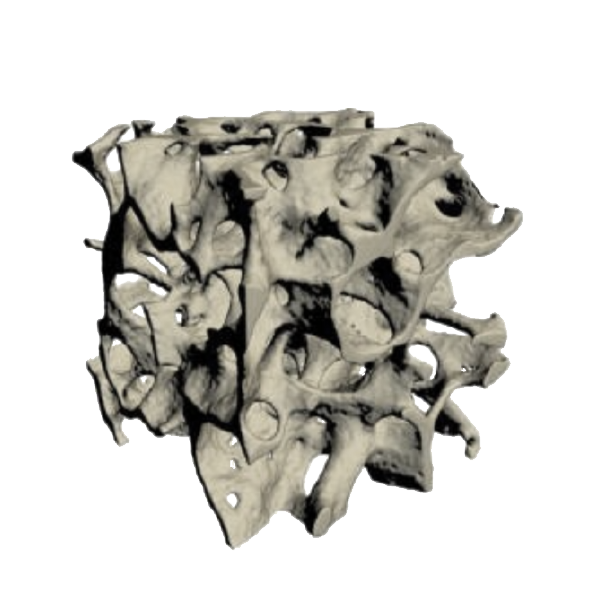
Control
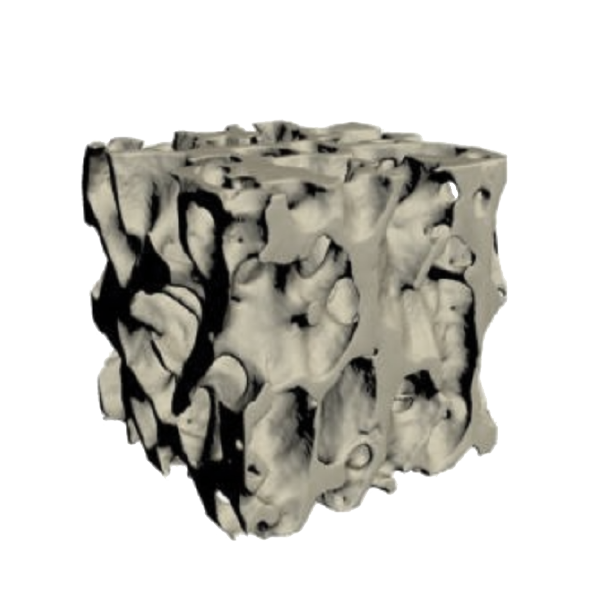
Hypoparathyroidism
Reprinted from Arquivos Brasileiros de Endocrinologia e Metabologia, 54(2), Rubin MR, Bilezikian JP, Hypoparathyroidism: clinical features, skeletal microstructure and parathyroid hormone replacement, 220-226, Copyright 2010, with permission from Elsevier.
Micro-CT images of trabecular bone from a patient with hypoparathyroidism and a control subject: Note the higher trabecular bone volume, number, and thickness in the image labeled Hypoparathyroidism.9
PTH deficiency disrupts1,2:
- Physiological access to calcium reservoirs in the bone
- The regulation of osteoclast and osteoblast activity
- Bone remodeling, leading to hypermature bone that may be more prone to fractures